Install an X.509 Certificate
The following article shows how to install an X.509 certificate for transport encryption.
The installation of an X.509 certificate is required to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) and secure authentication with Xtract Universal.
About X.509 Certificates
There are two main approaches for creating an X.509 certificate:
- Certificate released by an (internal) certification authority (CA)
- Self-signed certificate
On test environments you can use a self-signed certificate. For production environment it is recommended to use a certificate released by an (internal) certificate authority (CA).
Create and Import the X.509 Certificate
Make sure to have a TLS certificate issued by your IT network team considering the following points:
- The certificate property “Subject Alternative Name” contains the DNS name of the server that runs the XtractUniversal Windows service. When activating TLS, the Subject Alternative Name is used as the new hostname.
- The certificate common name (CN) attribute contains the DNS name of the server. To display the Common Name (CN) of the certificate, double-click the certificate in the Cetrificate Manager and navigate to the Details tab.
- Import the certificate to the Windows Certificate Store of the machine, that runs the XtractUniversal Windows service using the Microsoft Management Console (mmc.exe). The depicted example uses the server name "TODD":
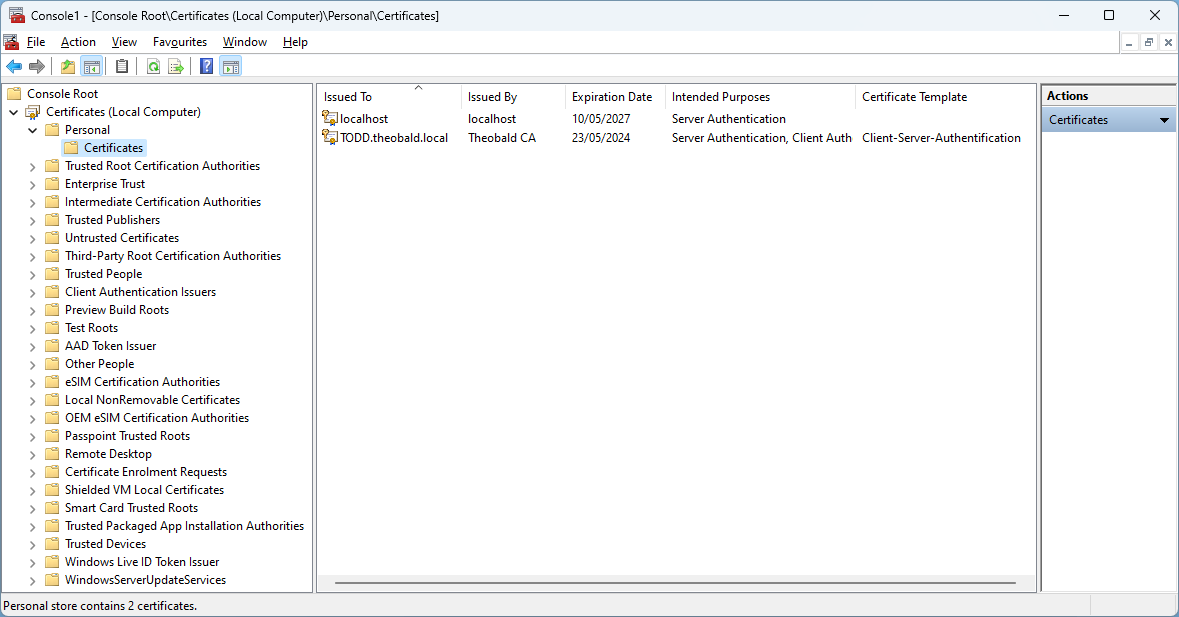
- Right-click the certificate and navigate to All Tasks > Manage private keys to add a new permission entry for the Windows user that runs the XtractUniversal Windows service.
- Enter the object name "NT Service\XtractUniversal Service" and click [Check Names] before applying the changes.
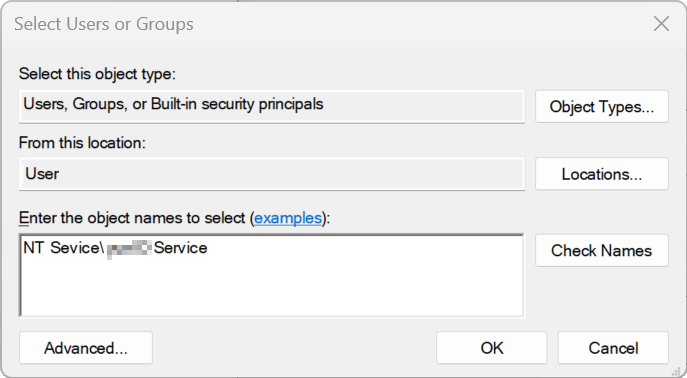
The certificate is now available on your machine.
Note
The Windows Certificate Store works with most browsers. NMozilla Firefox offers its own certificate storage. Configure your Firefox browser to trust certificates in the Windows certificate store or import the certificate via an enterprise policy, see Mozilla Support: Setting Up Certificate Authorities (CAs) in Firefox.
Integrate the X.509 Certificate
- Open Server > Settings from the main window of the Designer.
- In the tab Web Server, click [Select X.509 certificate]. The window "Edit certificate location" opens.
- Select the X.509 certificate created for your machine under Local Machine > Personal.
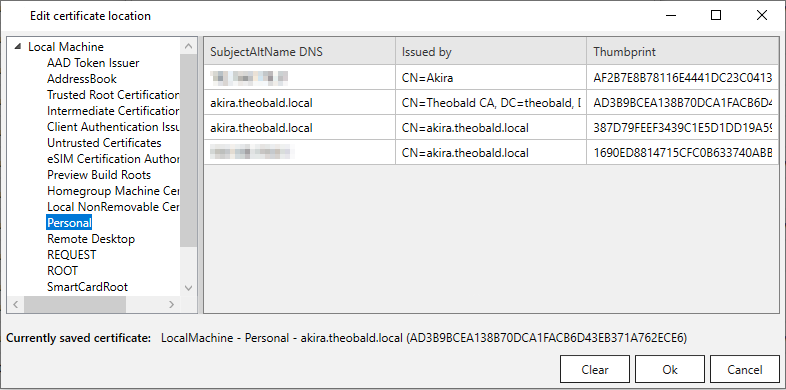
- Click [OK] to confirm your input. If prompted, restart the server.
The Xtract Universal server is now accessible via https protocol.
Related Topics
- Knowledge Base Article: Enable Secure Network Communication (SNC) via X.509 certificate
- Change Service Account
Last update: June 16, 2025